Natura 2000 for Young People
That’s what Natura 2000 is all about
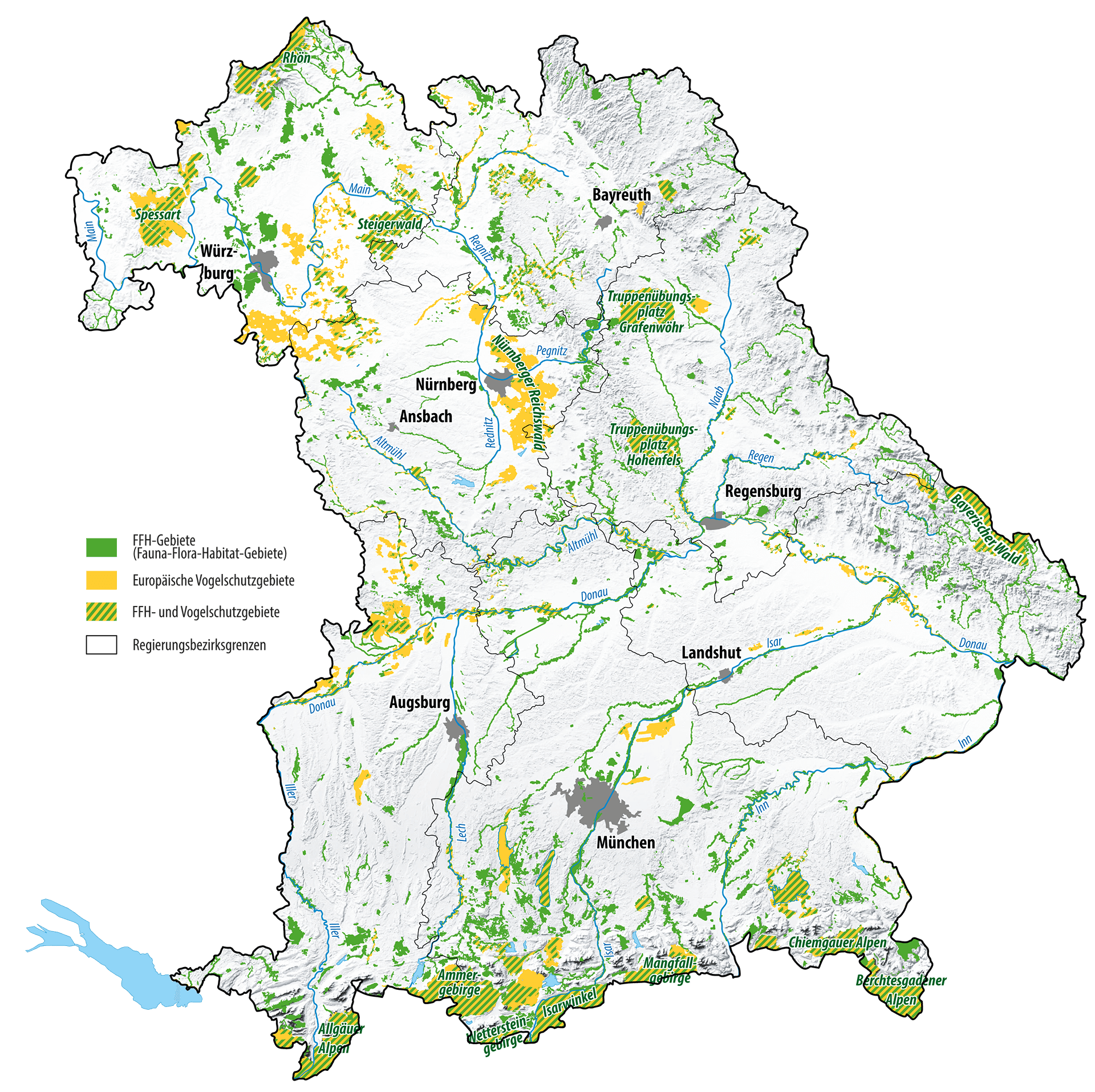
Natura 2000 is a coherent network of more than 27,000 protected areas throughout Europe. All these sites together cover about one fifth of the EU’s territory. This makes Natura 2000 the largest biodiversity protection project in the world. Natura 2000 sites are individual sites in nature.
These sites are important habitats for rare animal and plant species in Europe and are therefore protected by the European Union. Natura 2000 sites include protected areas for birds (bird sanctuaries) and areas that are rare natural habitats for other wildlife and plants. These are called FFH areas. The abbreviation FFH stands for Fauna-Flora-Habitate. Fauna: these are the animals that live in a Natura 2000 area. Flora: these are the plants that live in a Natura 2000 area.
Habitat: this is the place in which a plant or animal lives.

Learn and experience more
Learn more about the location of Natura 2000 sites in the Natura 2000 Network Viewer. You will also find an overview of Natura 2000 habitats and animal and plant species.
Learn more about the Natura 2000 student campaign and the exciting story of Fritz the Partridge:

What needs to be taken into account in Natura 2000 sites?
Bavaria’s rich, diverse natural environment and its preservation as the basis of life for future generations is what moves people in Bavaria. Natura 2000 was created more than 25 years ago as a European project in the course of the Rio de Janeiro World Summit. It is the most important nature conservation instrument in the European Union and, as a unique ecological network, aims to preserve our valuable natural capital.

Natura 2000 guarantees that the most beautiful Bavarian landscapes with their diversity are preserved and that they are managed or cared for in a sustainable way. Natura 2000 protects our attractive living environment. Natura 2000 areas offer recreation and nature enjoyment.
Natura 2000 protects everything that makes up our lives. The world’s largest nature conservation project preserves our Bavarian landscape, our animal and plant diversity. As a result, many small and large successes have already been achieved.
Who takes care of Natura 2000 sites?
The protected areas are intended to provide a safe home for many animal and plant species. For this to be the case, someone must take care of the areas. This is done by nature conservation experts. In Bavaria, so-called area managers help with this.
What is actually being done in Natura 2000 areas?
For each Natura 2000 site there is an established plan. This plan sets out how the area must be maintained so that it is a good habitat for the wild animal and plant species that live there.
The plans propose and present habitat improvements. The nature conservation experts will then know which habitat and which animal or plant species must be protected in the Natura 2000 area.
Do we really need the Natura 2000 areas?
Many people think that it would be better not to protect the Natura 2000 areas and instead build roads, buildings or ski resorts there. That’s how you could earn money. There are even groups of people who want to abolish Natura 2000. This would endanger the habitat of many animal and plant species.
We still have a lot of work to do to ensure that this does not happen and that the Natura 2000 network of protected areas is preserved in Europe. Although Europe covers only about 5% of the surface of our planet, it is home to a unique variety of wildlife, plants and landscapes that are unique to this region and nowhere else in the world, such as the Abruzzo chamois, the brown bear, the European pond turtle, rare butterflies and the dormouse.

What is the purpose of Natura 2000?
All people living in EU countries, whether farmers, forest owners or nature lovers, together protect their nature in Europe. Animals, plants and their habitats are protected together so that everyone can experience the natural treasures of Europe!
Natura 2000 is good for nature and people: For nature lovers and all other people and for the animal and plant species in Europe. The EU states have committed themselves to protecting and preserving animals, plants and habitats so that all people can experience Europe’s natural treasures.
Preserve the diversity of nature in Europe!
Biodiversity means a variety of natural life. So a variety of animals, plants, fungi and microorganisms and a variety of habitats in which they occur. But also a diversity within a species. The more different habitats there are, the more animal and plant species there can be. If the habitat of a species disappears, the species can disappear forever.
All living beings on our earth are important and part of our nature. Nature and its diversity are very important for humans, because nature provides them with clean water, food, raw materials from which we can produce houses, clothing and much more. Therefore, nature with all living beings is not only exciting and beautiful, but it is also our basis of life. In Europe alone there are over 130,000 species of land animals. We must preserve this diversity!