Natura 2000 – a protective roof for our European natural heritage
Encompassing pristine peat bogs, extensive riverine alluvial forests, Mediterranean beaches, the spectacular Wadden Sea and magnificent mountain peaks of the Alps – Europe is home to a high natural diversity. At the same time, species-rich cultural landscapes – stone walls, vineyards, middle forests or orchards all of which were created by human use- are part of Europe’s landscape offering habitats to a wide variety of animal and plant species.
Natura 2000 represents a network of protected areas to safeguard all of this – our European natural heritage- in all EU Member States. Natura 2000 represents a network of protected areas to safeguard all of this – our European natural heritage- in all EU Member States. In addition to the above mentioned ‘FFH’ sites, there are also protection areas in Europe that have been specifically selected as sanctuaries for birds. They represent the second important part of Natura 2000 territories. On the other hand, Natura 2000 also protects individual animal and plant species that have become rare in Europe or only occur in Europe.
In order to preserve the diversity of nature throughout Europe, the European Member States have selected FFH sites and bird protection areas in their countries that collectively constitute the Natura 2000 network. Under the European Habitats and Birds Directive, the protected areas thereby provide the European contribution to the implementation of the “Convention on Biological Diversity” agreed at the United Nations Conference on Environment in Rio de Janeiro in 1992. In total, there are approximately 27,000 FFH and bird protection sites in Europe, which corresponds to almost one fifth of Europe’s terrestrial area.
In a nutshell what Natura 2000 stands for
Natura 2000 in the 7 Bavarian Districts
More about Natura 2000 in the Bavarian Districts can be found in brochures of the seven regional governments. In these brochures, every district presents its unique natural heritage: Search for the region in Bavaria that interests you. Then click on the picture and you will be redirected to the free order form:
Natura 2000 creates and preserves values: for the people in the region – and for society
For the people of Europe, nature is also the basis of their daily life. Every day, nature provides everything that we need to live at no cost to us: from clean air and water to insects that pollinate our fruit trees. At the same time, we use nature in our free time and for our recreation. The basic idea of Natura 2000, the European network of protected areas, is to preserve this priceless and unique resource for current and future generations in Europe.
The preservation of our essential natural assets represents an important task of every generation – for the generations to come. Natura 2000 creates an effective framework, because areas within the network provide clean water, prevent erosion and help to prevent landslides or floods. Intact ecosystems and biomass, wood and agricultural land use ensure income in many rural areas. Natura 2000 means securing our precious natural capital: The European Commission estimates that these services from the Natura 2000 sites amount to several hundred billion euros per year.
The Natura 2000 sites represent Europe’s natural capital and most attractive landscapes – a majority of which are particularly valuable for tourism and recreation and therefore contribute significantly to the creation of local socio-economic value. Thus, structured use and management of these landscapes preserves and creates value. Landscapes serving as tourism destinations are dependent on protection in order to deliver added value from nature. Natura 2000 ensures a sustainable and nature-friendly use of these areas, now and in the future.
The historically rooted rural land use has often created particularly attractive landscapes and habitats in Europe: species-rich meadows, heathlands and alpine pastures. In the areas protected by Natura 2000, agriculture and forestry as well as fishing and hunting are possible – and welcomed. Without land use many cultural landscapes would be lost, since they were generated through traditional farming methods.
Agriculture and forestry, fishermen and hunters are all important partners in the implementation of Natura 2000, especially in the conservation of habitats and species. Owners such as farmers and foresters often play a key role in the Natura 2000 areas. Their commitment is crucial when it comes to maintaining or improving Natura 2000 sites. The state supports them with agro-environmental programs and other financial resources. As a general rule, the principles of cooperation and voluntary participation apply here.
Nature conservation in the context of Natura 2000 thus means that historically developed cultural landscapes are preserved with regard to their function for farmers and their appeal for people seeking relaxation.
Natura 2000 thus substantially contributes to preservation of diversity within these landscapes and, at the same time, to their sustainable cultivation or maintenance.

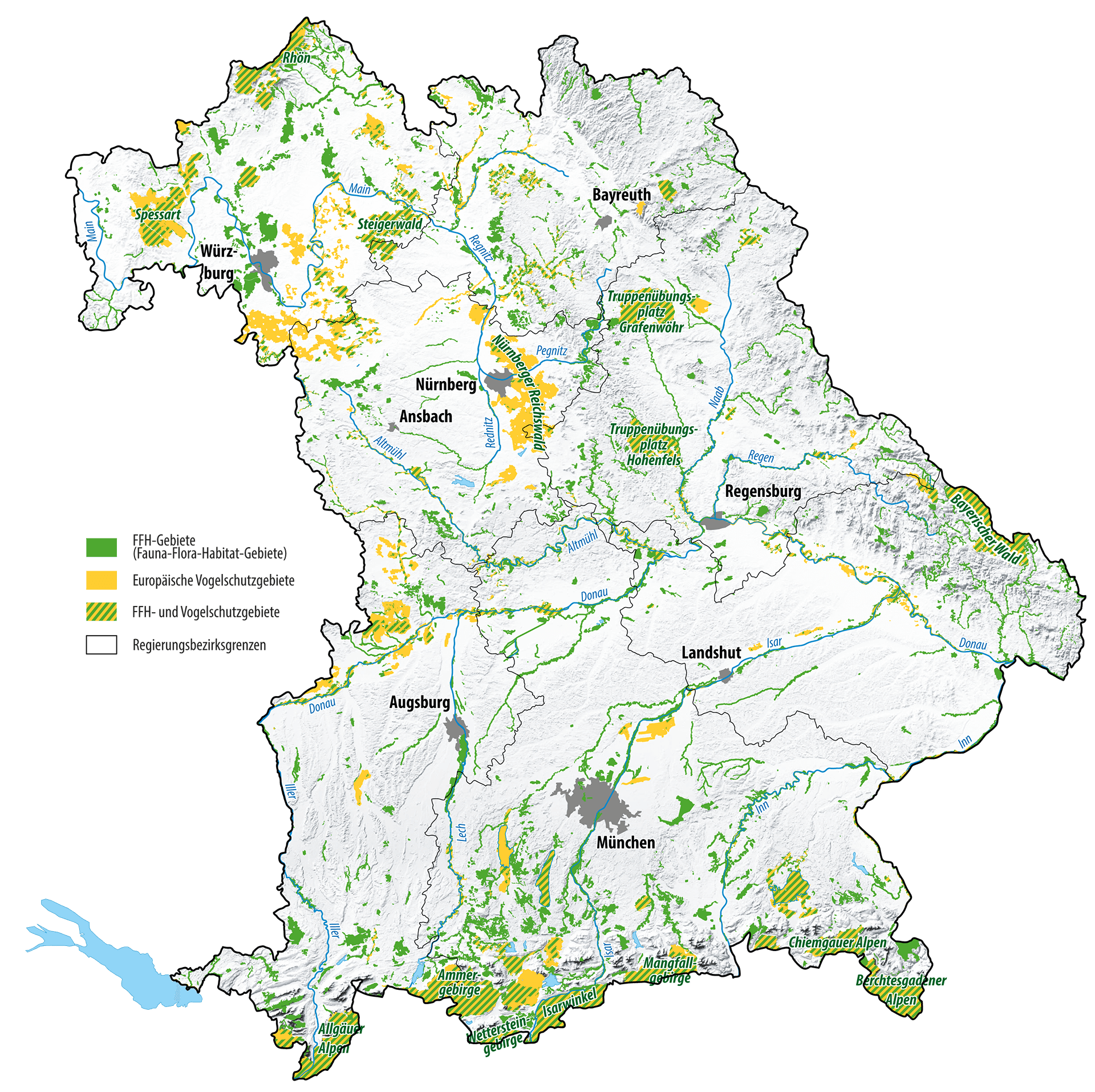
The Natura 2000 network in Bavaria
There are 674 Natura 2000 areas in Bavaria. These are FFH areas (green), areas covered by the European Birds Directive (orange) and areas protected by both directives (shaded areas).
Find local Natura 2000 areas on your doorstep: Just click on the map to find the nearest Natura 2000 site in your region using the ‘Bayernatlas’. You can use the search bar to find a place or try the zoom function on the map.
Here, experts can explore the European Natura 2000 network.
Our European natural heritage in Bavaria
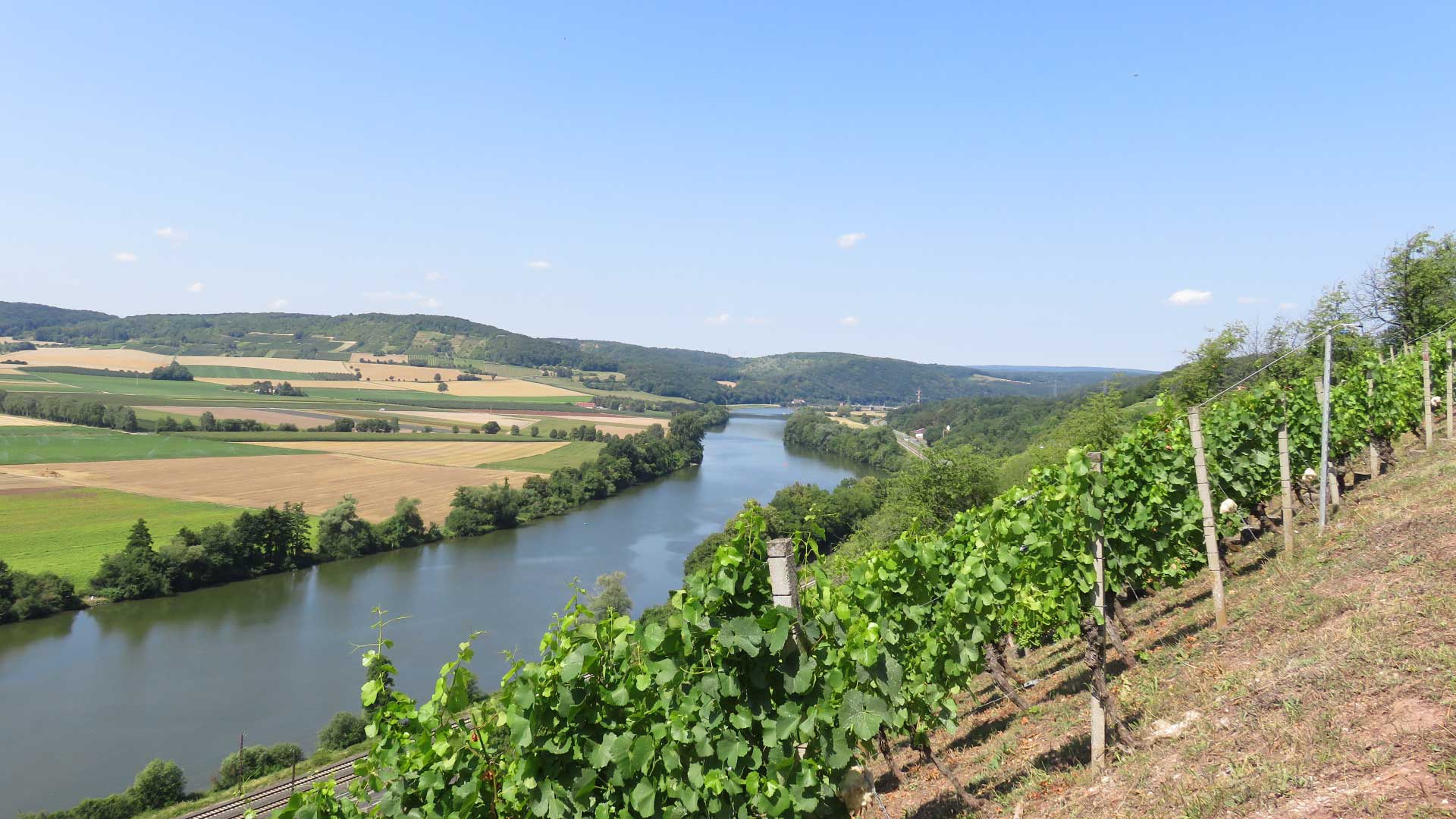
As the largest federal state in Germany, Bavaria is home to a variety of landscapes between the river Main and the Northern Limestone Alps: The Main valley with its wine-growing regions, the Franconian stratum region, wooded low mountain ranges such as the Bavarian Forest, cultural landscapes such as the Hallertau hop growing region, the Alps and the foothills of the Alps. These diverse landscapes make Bavaria an extremely popular tourism destination in Germany.
Bavaria comprises the majority of Natura 2000 sites in Germany. The sites cover around 11% of Bavaria’s surface area and are distributed amongst the seven Bavarian administrative districts with a total area of 800,000 hectares.
In the Natura 2000 areas, Bavaria displays all its beauty and diversity: from flowering meadows to dry vineyards, river valleys, bogs and lakes, and rugged mountain peaks. This diversity of habitats is home to over 250 animal and plant species protected by Natura 2000 in Bavaria. Here you will find many rare butterflies, dragonflies and bat species or unique orchids. Moreover, Bavaria is home to a variety of species that occur only here.
Many of Bavaria´s natural assets are thus included in Natura 2000. As part of the European protected area network Natura 2000, they signify Bavarian natural heritage. Bavaria thus contributes its most valuable natural capital to Natura 2000.




Natura 2000 in Bavaria relies on partnerships
Traditional land use has strongly influenced the landscape and has produced a particular diversity of nature in many places in Bavaria. A significant proportion of Natura 2000 areas are located in such historic cultural landscapes, requiring the commitment of all to preserve species and their natural habitats and to secure the landscape. Natura 2000 in Bavaria relies on a partnership-based commitment from the various groups and institutions involved, such as municipalities, farmers and foresters and NGOs.
Cooperative development and management of the Natura 2000 sites is essential in Bavaria. Round Tables in all Natura 2000 sites provide the opportunity for officials, NGOs, farmers and landowners to meet and to develop common approaches for the management of Natura 2000 sites. This approach has already been successful in many projects, as it provides the foundation for reliable Natura 2000 partnerships.
Many municipalities and associations, together with the support of owners and managers, have implemented best-practice conservation and development projects for Natura 2000 sites. In this way, significant results have ben achieved for the Bavarian nature. The State rewards conservation and management of Natura 2000 sites, thus enabling the farmers or owners to generate income from agriculture and forestry. Natura 2000 in Bavaria contributes to sustainable agriculture and forestry, preserving habitats as well as animal and plant species.
In 2017 alone, the Free State of Bavaria invested about 31 million euros to various focussed funding programs in order to support cooperation, voluntary stakeholder commitment and the implementation of Natura 2000. Since the beginning of Natura 2000, 25 EU-LIFE projects have been carried out in Bavaria with a volume of more than 45 million euros. These projects contribute to the implementation of Natura 2000 in Bavaria and are co-funded by the European Union. Learn more about the LIFE projects in Bavaria.

Technical papers and general information on Natura 2000 in Bavaria
A comprehensive compilation of technical contributions to Natura 2000 can be found in the special edition of ‘ANLiegen Natur’ as well as on the webpages of the Bavarian Environment Agency and the Bavarian State Ministry of the Environment and Consumer Protection.